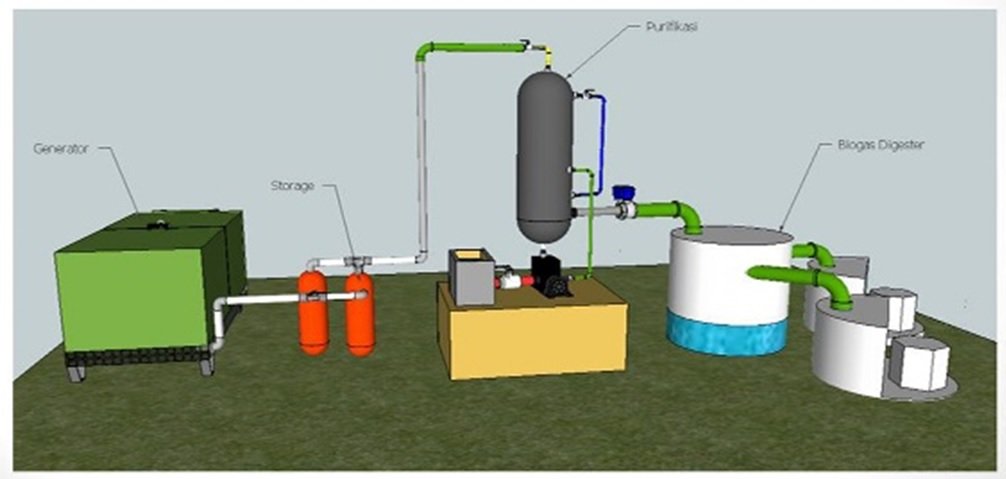
Biogas, a renewable energy source produced through anaerobic digestion of organic waste, has gained significant attention as an alternative to fossil fuels. It is primarily composed of methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), with trace amounts of other gases and impurities. To unlock the full potential of biogas for biofuel production, it is essential to purify it, enhancing the methane content and ensuring its quality for various energy applications. In this article, we explore advanced biogas purification techniques, their importance, and how they contribute to high-quality biofuel production.
The Importance of Biogas Purification
Raw biogas, while an excellent source of energy, typically contains contaminants that reduce its energy content and pose challenges in its use for electricity generation, heating, and transportation. The methane in biogas is the valuable component, but impurities like CO₂, hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), water vapor, and siloxanes can lower its energy density and cause operational issues in engines, turbines, and other biogas-powered equipment. Biogas purification aims to remove these impurities, resulting in higher methane concentration, which maximizes energy output and ensures the gas is safe for use.
Effective purification techniques enable the production of biomethane, which can be injected into the natural gas grid or used as a substitute for compressed natural gas (CNG) in vehicles, offering a cleaner, greener alternative to fossil fuels.
Key Contaminants in Raw Biogas
Before discussing purification methods, it’s important to understand the key contaminants found in raw biogas that need to be removed:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO₂):
While CO₂ is not harmful to equipment, it dilutes the methane content, decreasing the energy potential of biogas. Biogas with high CO₂ content has lower heating value, reducing its effectiveness in energy generation. - Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S):
Hydrogen sulfide is a toxic, corrosive gas that can damage engines, pipelines, and other biogas-utilizing equipment. It also contributes to the formation of sulfuric acid, which accelerates corrosion and reduces the lifespan of equipment. - Water Vapor:
Excessive moisture in biogas can lead to corrosion, equipment failure, and reduced efficiency in combustion processes. Moisture can also cause blockages and maintenance issues in pipes and valves. - Siloxanes:
Siloxanes, primarily found in biogas from wastewater treatment and food waste, are organic compounds that contain silicon. When burned, siloxanes can form silica, which can damage engines and turbines. - Ammonia (NH₃):
Ammonia, often found in biogas from agricultural waste, is toxic to certain biogas upgrading technologies. It can also contribute to equipment corrosion. - Oxygen (O₂):
Oxygen dilutes the methane content and can lead to hazardous combustion conditions, such as fire or explosion risks. Removing oxygen from biogas is crucial for safe and efficient energy production.
Advanced Biogas Purification Techniques
Several advanced biogas purification methods are used to remove contaminants, enhance methane content, and produce high-quality biomethane. These techniques vary in their approach and effectiveness, depending on the specific impurities present.
1. Water Scrubbing
Water scrubbing is a widely used technique for removing CO₂ and other water-soluble contaminants like ammonia from biogas. In this process, raw biogas is passed through water under pressure, where CO₂ and other impurities are absorbed, leaving behind purified methane. The process can be highly efficient and is commonly used in large-scale biogas plants. After absorption, the CO₂-saturated water is regenerated, and the methane is separated for further use.
2. Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA)
Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) is an effective method for separating methane from CO₂ and other trace gases like oxygen and nitrogen. In PSA, biogas is passed through a bed of adsorbent materials (such as activated carbon or zeolite) under high pressure. These materials adsorb the impurities, while methane passes through. By reducing the pressure, the adsorbed contaminants are released, allowing for continuous purification. PSA is particularly useful for achieving high-purity methane for biomethane production.
3. Chemical Scrubbing
Chemical scrubbing uses an alkaline solution to absorb impurities such as hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) and siloxanes from biogas. For instance, sodium hydroxide (NaOH) can react with H₂S to form harmless byproducts like sodium sulfide, which can be easily disposed of. Chemical scrubbing is highly effective for removing acidic gases and is often used in combination with other purification methods to produce high-quality biogas.
4. Membrane Separation
Membrane separation is a technique that utilizes selective permeability to separate methane from other gases in biogas. Membranes with specific pore sizes allow smaller molecules like CO₂ and H₂S to pass through while retaining larger methane molecules. This method is highly efficient, especially for high-purity biomethane production. It can be used in combination with other technologies for a more comprehensive biogas purification process.
5. Biological Scrubbing
Biological scrubbing leverages the natural ability of microorganisms to remove impurities from biogas. In this process, biogas is passed through a bioreactor containing bacteria that metabolize contaminants such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia. These bacteria convert harmful gases into non-toxic substances, making the biogas suitable for use in energy production. Biological scrubbing is an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for purifying biogas, with the added benefit of being sustainable.
6. Cryogenic Separation
Cryogenic separation uses low temperatures to condense and separate components of biogas. CO₂ and other impurities can be liquefied and removed at very low temperatures, while methane remains in its gaseous state. This technique is particularly effective for large-scale biomethane production and can achieve very high purity levels.
Benefits of Biogas Purification
The main benefits of biogas purification include:
- Increased Energy Output:
By removing CO₂ and other impurities, biogas purification increases the methane concentration, leading to higher energy production from the same volume of biogas. This boosts the overall efficiency of renewable energy generation. - Enhanced Equipment Longevity:
Purified biogas is less corrosive and reduces the risk of damage to engines, turbines, and other equipment used in biogas energy systems. This leads to reduced maintenance costs and extended operational life. - Regulatory Compliance:
Many regions have regulations regarding the quality of biogas used for energy applications, such as grid injection and transportation. Purification ensures biogas meets these standards, making it suitable for various uses, including biomethane production. - Environmental Benefits:
High-quality biomethane is a cleaner alternative to natural gas, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and supporting the transition to a more sustainable energy system. - Economic Viability:
By producing high-quality biomethane, biogas plants can access new markets and improve the profitability of renewable energy projects. Purified biogas can be sold as a high-value biofuel, providing an additional revenue stream.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While biogas purification technologies have advanced significantly, there are still challenges to overcome. The cost of purification systems, energy consumption, and the need for specialized equipment remain barriers, particularly for small-scale biogas producers. Additionally, the variability in raw biogas composition means that purification systems must be adaptable and efficient across different feedstock types.
However, ongoing research and development in biogas purification technologies are expected to address these challenges. Innovations in membrane technology, biological scrubbing, and hybrid purification systems hold great promise for reducing costs, improving efficiency, and increasing the scalability of biogas purification.
Conclusion
Biogas purification is a crucial step in optimizing the potential of biogas as a renewable energy source. Advanced purification techniques, such as water scrubbing, PSA, chemical scrubbing, and membrane separation, ensure that biogas is refined to a high-quality biomethane, suitable for a wide range of energy applications. By removing impurities like CO₂, H₂S, and siloxanes, biogas purification enhances energy production, protects equipment, and contributes to a more sustainable energy future. With continued advancements in purification technologies, biogas has the potential to play a key role in the global transition to renewable energy.