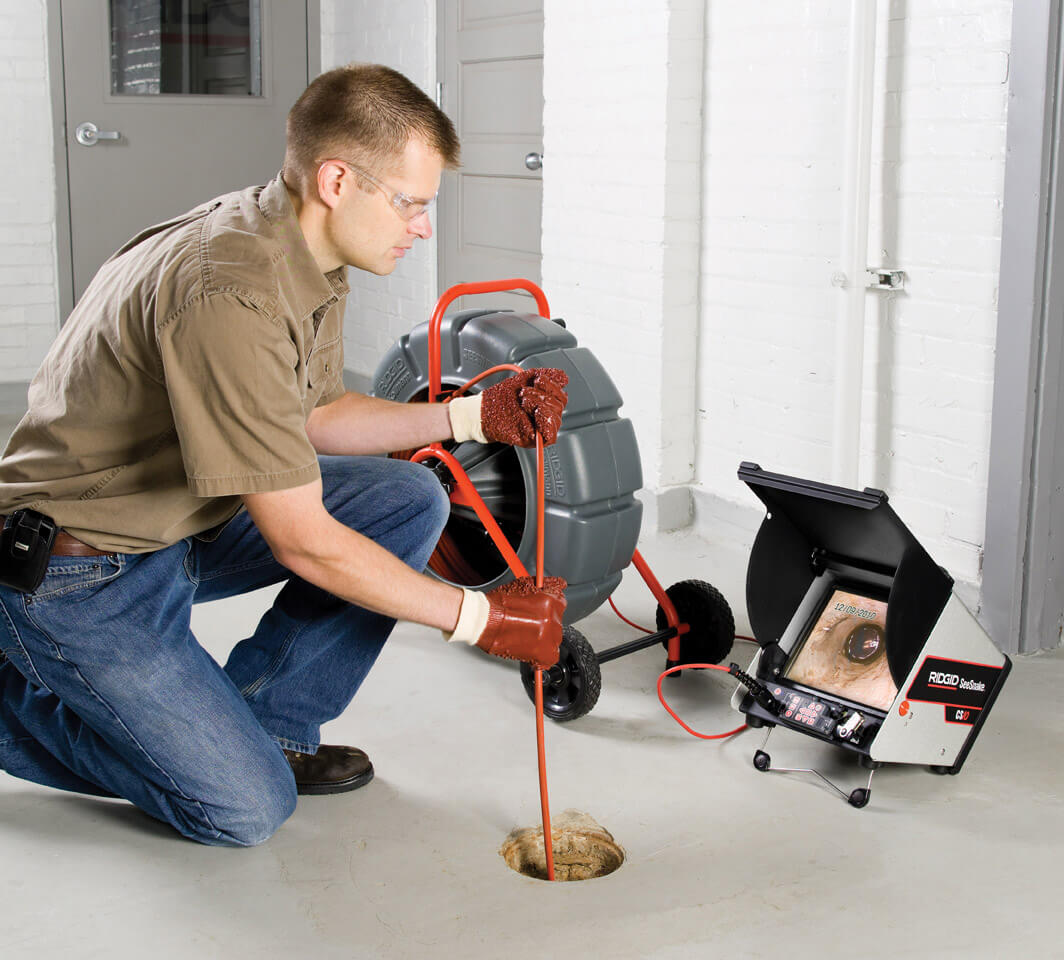
Pipe inspection cameras have become essential tools for plumbing professionals, municipal workers, and facility managers. They allow for accurate diagnostics of pipelines, enabling the detection of blockages, leaks, and structural issues without unnecessary excavation. However, to maximize their effectiveness and maintain safety, it is important to follow best practices during inspections. Proper use ensures reliable results, extends the lifespan of the equipment, and protects operators from potential hazards.
Preparing for an Inspection
Before deploying a Pipe Inspection Camera, it is essential to assess the site and pipeline conditions. Identify the type and size of the pipes, their material, and any potential obstacles that could affect the inspection. Clear the access points to allow smooth insertion of the camera and ensure that operators have a safe working environment. Reviewing previous maintenance records and schematics of the pipeline network helps anticipate problem areas and plan an efficient inspection route.
Ensuring Equipment Readiness
Checking the camera system before use is critical for safety and effective operation. Inspect cables, connectors, and the camera head for damage or wear. Confirm that the LED lighting functions properly, and ensure that monitors or recording devices are fully operational. For battery-powered units, verify sufficient charge to complete the inspection without interruption. Well-maintained equipment minimizes the risk of technical failures during critical inspections and ensures accurate visual feedback.
Safe Handling of the Camera
Pipe inspection cameras are sensitive instruments that require careful handling. When inserting or retracting the camera, avoid sharp bends or excessive force that could damage the push rod or cable. Use gloves to maintain grip and protect hands from contaminants. For cameras designed with pan-and-tilt or articulated heads, operate controls smoothly to prevent sudden movements that could harm the camera or pipeline. Maintaining gentle, controlled movement ensures the longevity of the equipment and produces stable, clear footage.
Proper Navigation Techniques
Effective navigation of the pipeline is key to obtaining comprehensive visual data. Advance the camera slowly through bends, junctions, and vertical sections to avoid snagging or misalignment. Use real-time video feedback to adjust the camera angle and focus on areas of interest. For longer pipelines, make incremental inspections, periodically retracting and reinserting the camera as needed to ensure complete coverage. Careful navigation enhances the accuracy of the inspection and reduces the risk of damage to the camera or pipes.
Maintaining Hygiene and Contamination Control
Pipe inspections often involve exposure to wastewater, debris, or chemical residues. It is essential to follow hygiene protocols to protect both operators and equipment. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, and eye protection. Clean and disinfect the camera and cables after each use to prevent cross-contamination between inspection sites. Proper sanitation practices also contribute to equipment longevity and operator safety.
Recording and Documenting Findings
Accurate documentation is a vital part of effective pipe inspections. Use the camera’s recording and snapshot features to capture images of blockages, leaks, or structural defects. Annotate footage when possible, noting pipe locations, measurements, and observations. Maintaining organized records facilitates future inspections, supports preventive maintenance programs, and provides evidence for repair planning or regulatory compliance.
Adhering to Manufacturer Guidelines
Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for camera operation and maintenance. These guidelines provide critical information on voltage limits, cable handling, cleaning procedures, and safe operational practices. Adhering to these instructions ensures optimal performance, reduces the risk of damage, and extends the service life of the pipe inspection camera.
Troubleshooting and Emergency Protocols
Operators should be trained in basic troubleshooting in case of camera malfunction, loss of video signal, or obstruction within the pipeline. Having a contingency plan, including spare cables, replacement parts, and contact with technical support, ensures minimal disruption during inspections. Quick, informed responses to issues prevent further damage and maintain the integrity of both the equipment and the pipeline.
Continuous Training and Skill Development
The effectiveness of a pipe inspection camera depends not only on the equipment but also on operator skill. Regular training sessions on camera handling, navigation techniques, and interpretation of visual data improve inspection quality. Familiarity with various pipeline types, common issues, and preventive maintenance strategies enhances efficiency and safety during operations.
Conclusion: Safe and Effective Pipe Inspections
Following best practices for using a pipe inspection camera ensures safe, efficient, and accurate inspections. Proper preparation, careful equipment handling, hygienic protocols, and detailed documentation contribute to reliable diagnostics and effective maintenance planning. Integrating these practices into routine inspection programs extends the lifespan of both pipelines and camera equipment, protects operators, and maximizes the value of modern pipe inspection technology.